Polyethylene Wax, referred to as PE Wax, is a thermoplastic polymer consisting of long ethylene monomer chains. Polyethylene is one of the most widely used plastics in the world, and PE wax has a large variety of uses and applications.
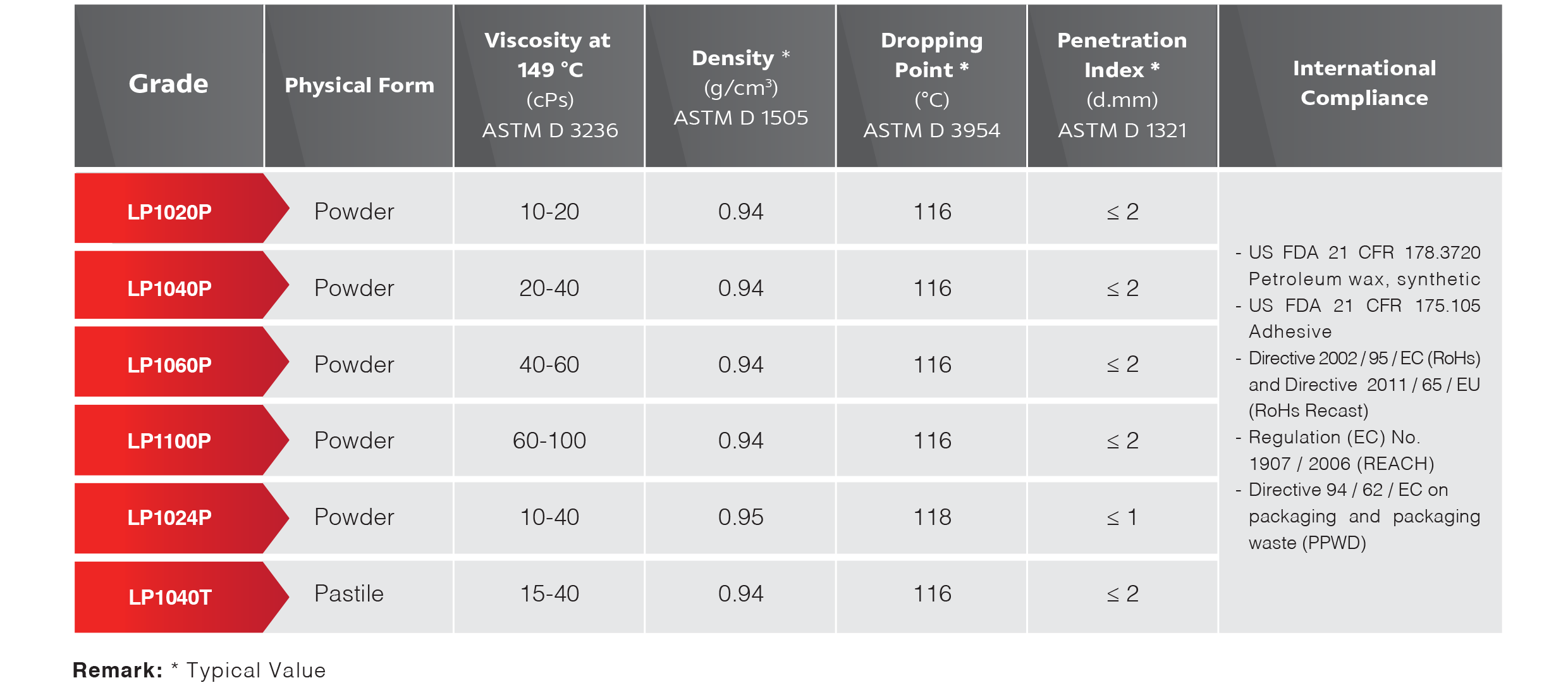
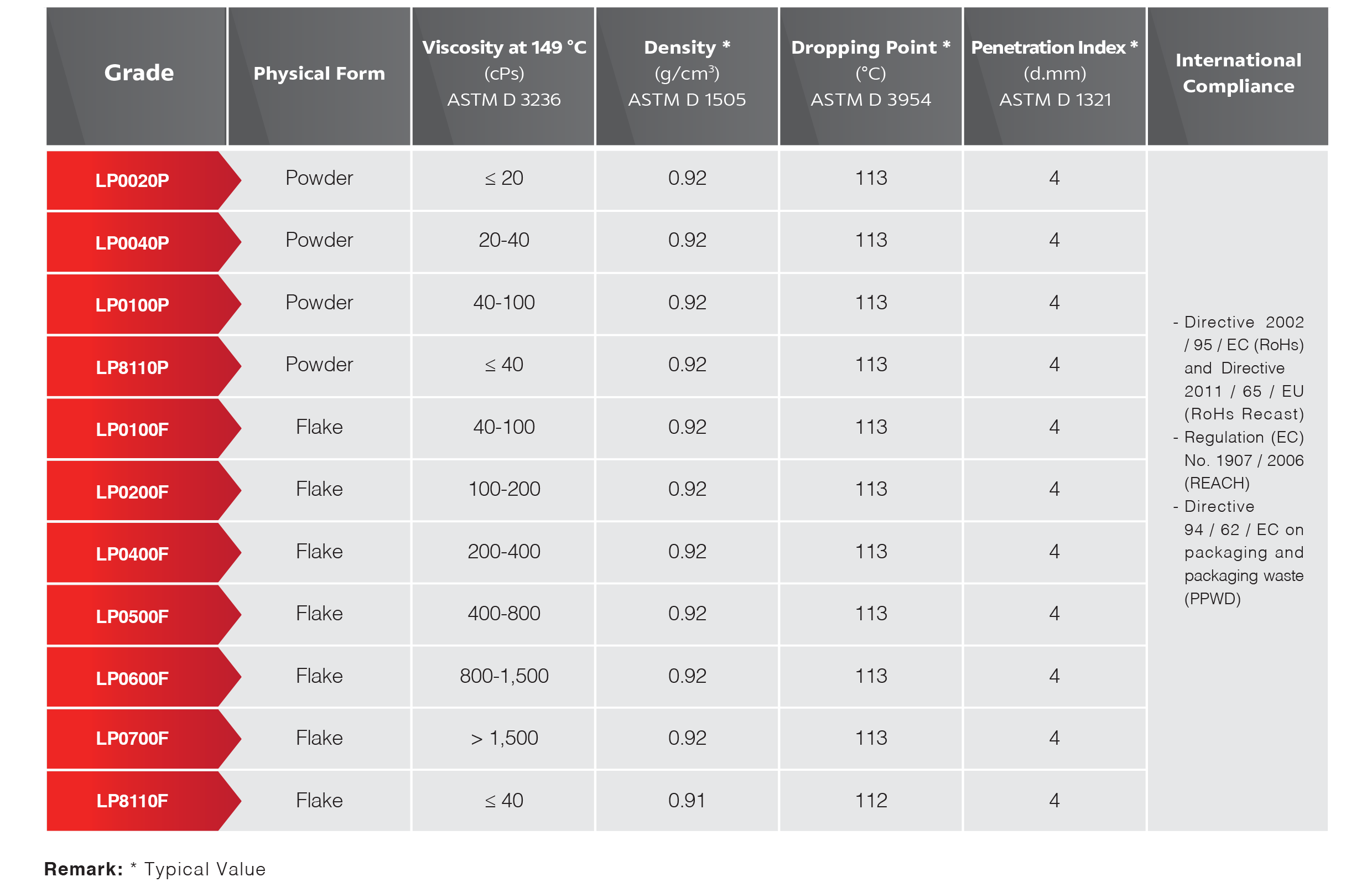
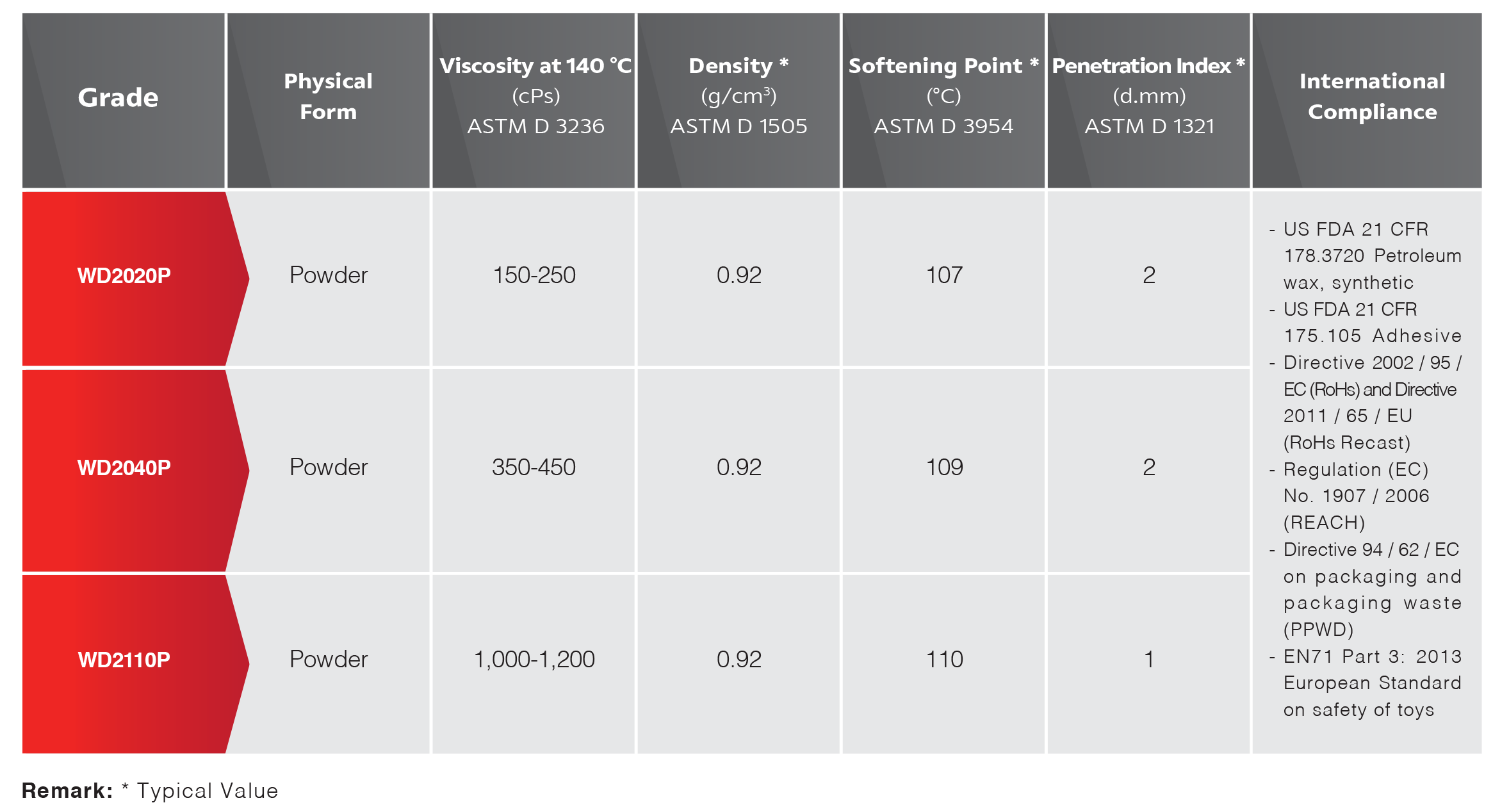
PE Wax is available from on-purpose production and as a byproduct of polyethylene production. This material is available in both HDPE and LDPE forms.

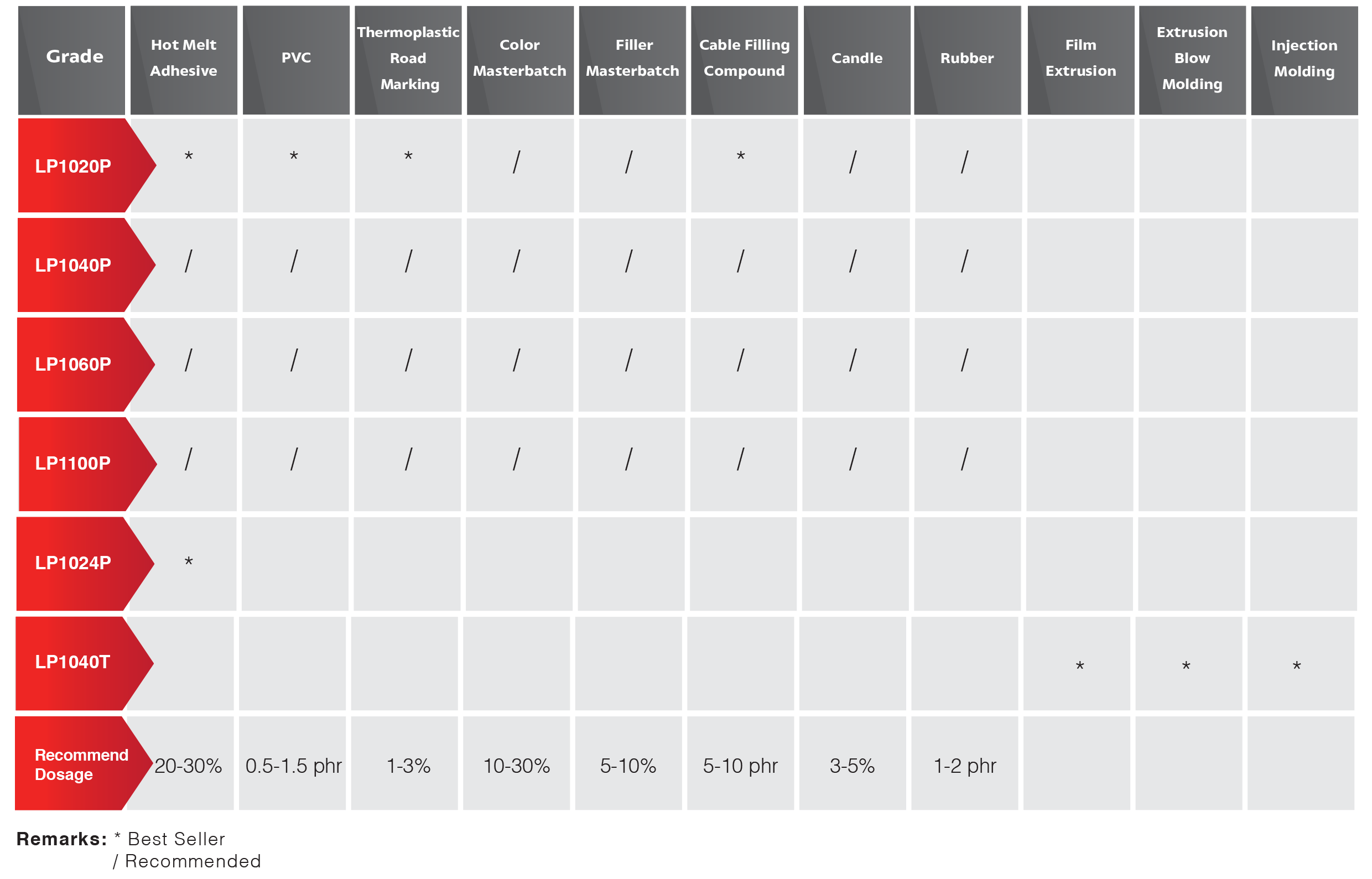
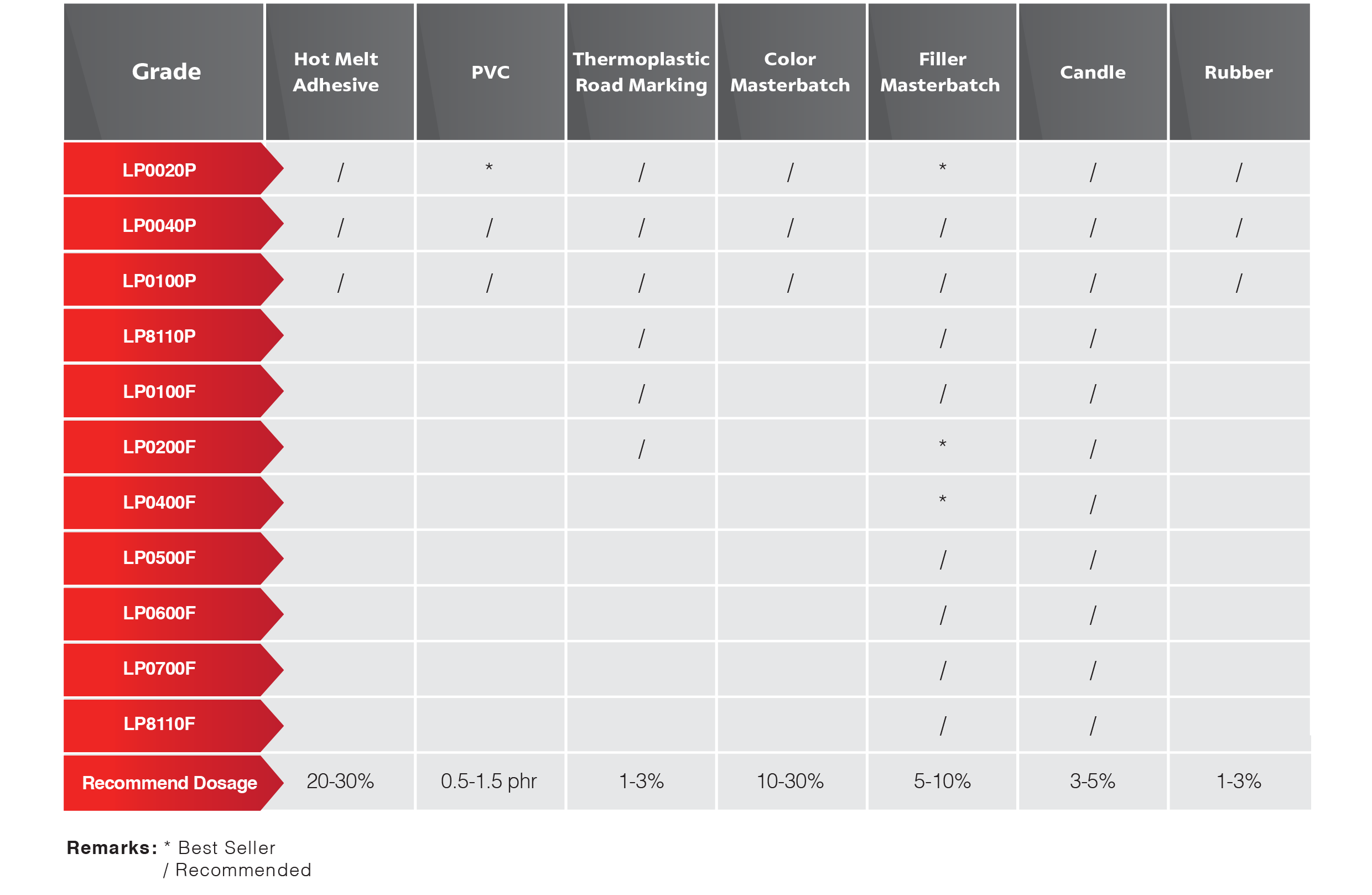
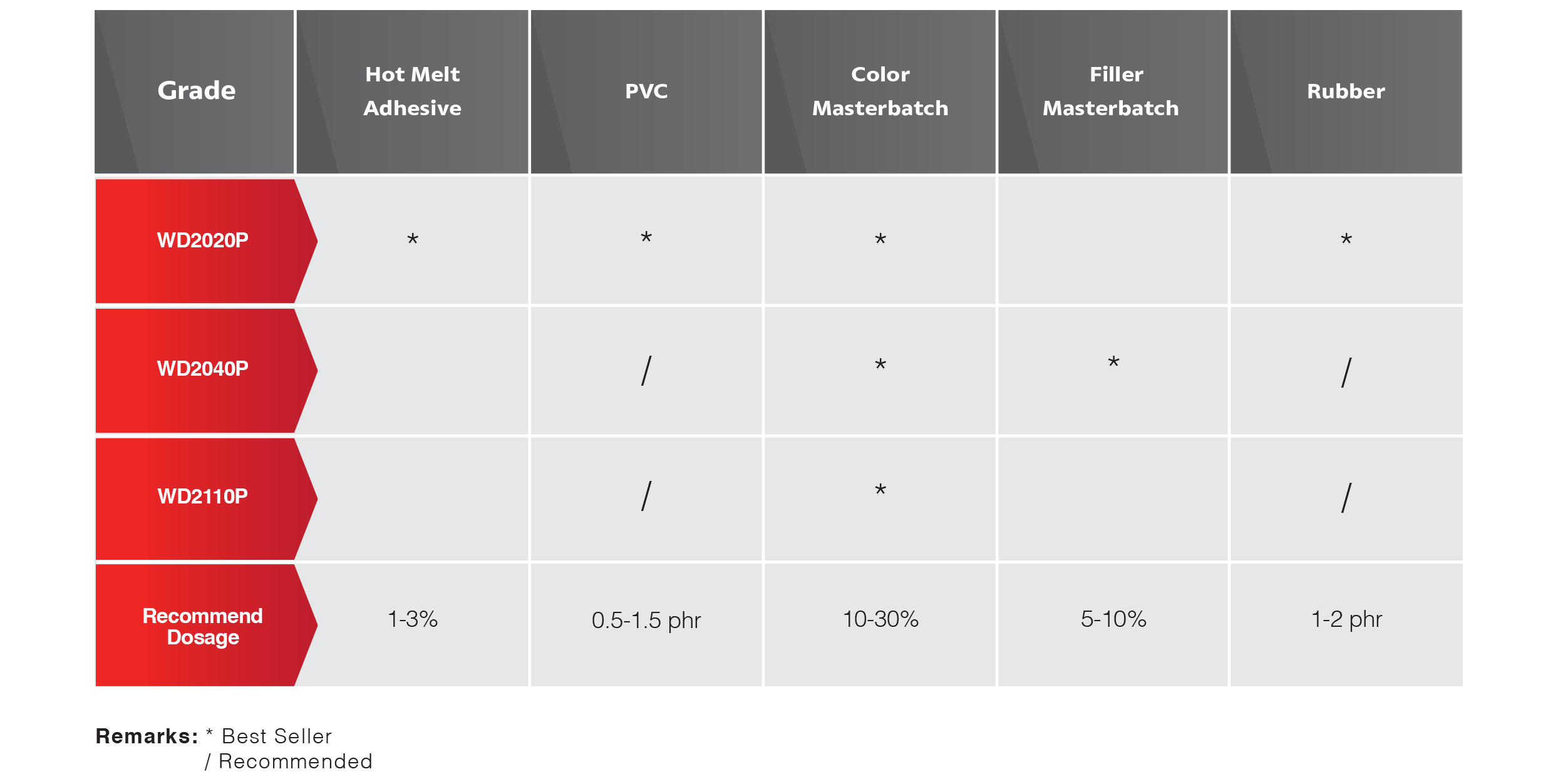
A recent survey by Transparency Market Research identified the PE wax market to include plastic additives, candles, cosmetics and rubber. Others are packaging, lubricants, wood and coatings.
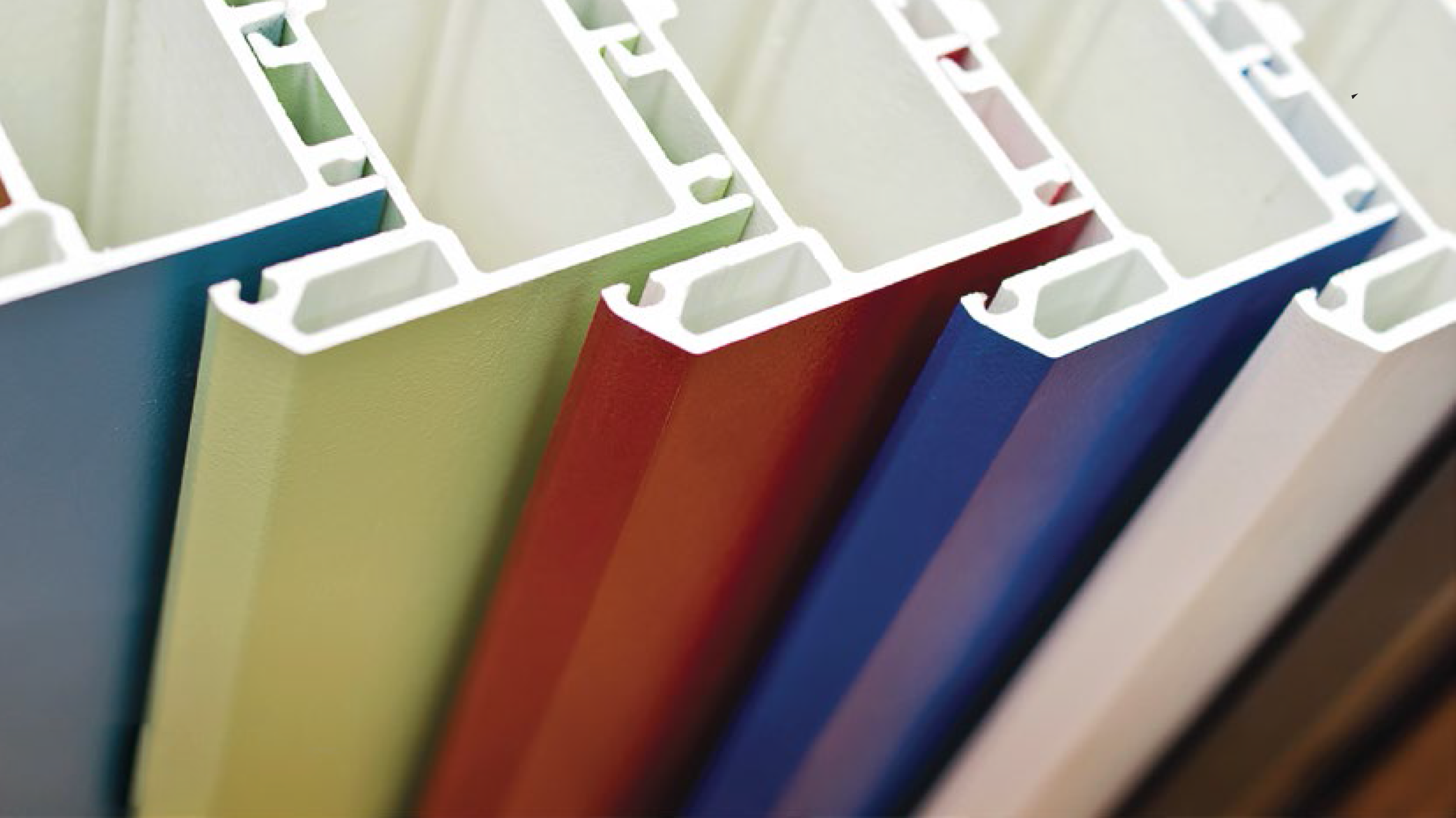
The wax finds application in a wide range of industries because of its desirable physical and chemical properties. As the material can have a broad range of melt points, densities and other properties, it is understandable why it is used so extensively.
The emulsifiable variety is particularly crucial in the textile industry. It is also used in paper coating, leather auxiliaries, crayons and cosmetics. The non-emulsifiable type is mostly common in printing ink, pigment concentrates and paints.
In the textile sector, the material probably finds the most intensive application. Emulsions made from the wax offer stable softening. While they resist acids and other chemicals, these emulsions are friendly to the fabric – with no yellowing of fabrics, no colour change and no chlorine retention.
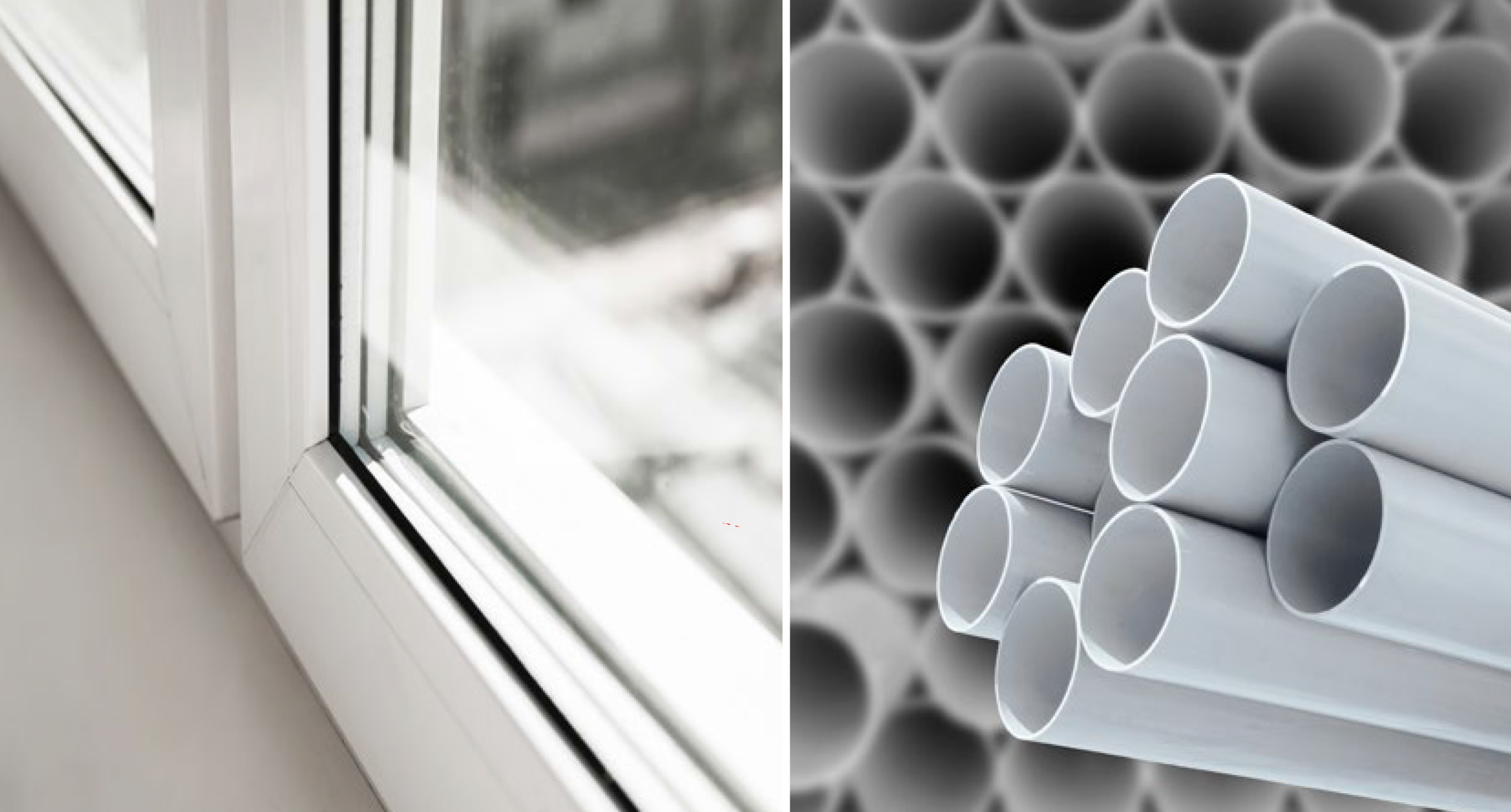
The packaging sector is also using polyethylene wax intensively. Adherence to the olefins regulations is necessary when using the material as a food additive, at least in the United States.
The coating industry has historically used waxes. The importance of wax is that it adds water-repellency, better slip, and mark resistance among other features.
- Anti-sagging
- Anti-settling
- Abrasion resistance
- Excellent gel forming
- Enhanced heat resistance
In the inks industry, the material presents similar advantages. Most ink types contain polyethylene wax as a way to improve the coefficient of friction and increase scuff resistance
- Adjustable open time and set time
- Enhanced heat resistance
- Reduced viscosity to promote wettability
- Improved the dispersion of pigments in plastic
- Higher pigment loading
- Enhanced color strength development
- Enhanced heat resistance
- Reduced viscosity
- Improved the dispersion of the component
- Improve the dispersion of filler
- Higher filler loading
- Delayed fusion time and reduced fusion torque
- Sharpened up dynamic heat stability
- Excellent external lubricant
- Excellent gel forming
- Enhanced heat resistance
- Inert agent